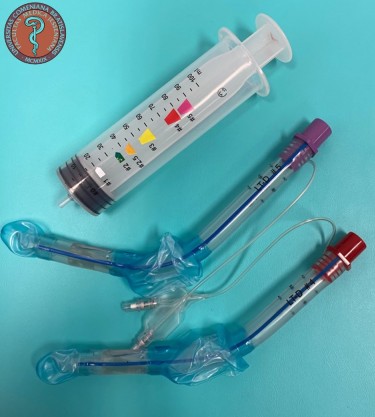
Laryngeal tubeThe Laryngeal Tube is a supraglottic airway device for securing the airway during difficult airway management as an alternative technique to mask ventilation and tracheal intubation. It is used in general anesthesia during spontaneous or positive pressure ventilation.
These devices are applied to the upper airways without the need for direct visualization of the oral cavity and supraglottic space. Their technical implementation is relatively simple, but they are already more advanced methods of securing airways.
The introduction of supraglottic devices requires more regular training. The devices have a tip inserted into the esophagus, which partially obscures it and thus reduces the probability of aspiration to the lungs. They can be connected to mechanical lung ventilation and EtCO2 sensor. The use of these aids is limited by the depth of unconsciousness. Deep unconsciousness is required for the tolerance of these devices in the supraglottic space - GCS 3b. With GCS more than 3b, the patient should be sedated and muscle relaxants should be used optimally. In the case of superficial sedation without muscle relaxation, there is a risk of provoking a gag reflex or laryngospasm.
Laryngeál tubes size 4 a 5. |
Map: Laryngeal tube EN (1747)
|
||
|
Review your pathway |